The internet is full of language learning advice—but which methods actually work? How can you learn a language efficiently while getting the best possible results? How do you make the most of your time while still enjoying the process?
To help you navigate your language learning journey, we’ve created a step-by-step framework that tells you what to focus on at each stage. With so many methods and resources available, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. But success isn’t about using every tool out there—it’s about choosing the right methods at the right time.
Here’s our proven framework for mastering any language efficiently. 🚀
1. Build a solid foundation
1.1 Vocabulary
Word Frequency

You may have heard of the Pareto principle applied to language learning: 80% of communication comes from just 20% of the total words. In other words, learning the 500–1,000 most common words can help you understand 60–80% of everyday speech and writing.
Many courses and apps don’t prioritize word frequency, which means you might end up learning less useful words first. But now that you’re aware of this, you can take control of your learning.
💡 Tip: Choose apps and resources that focus on high-frequency words. When using a textbook, don’t waste time memorizing obscure words—skip them and focus on what’s actually useful for real-life conversations.
Anki: The Best Tool for Vocabulary Retention
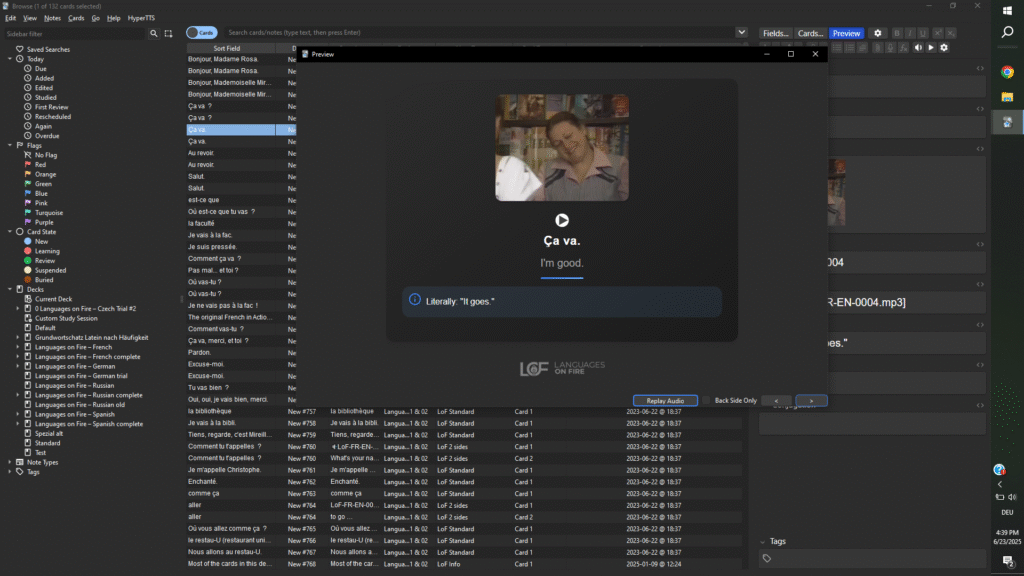
Anki is an essential tool for building vocabulary efficiently. It’s a flashcard app that uses spaced repetition to ensure you review words at the optimal time—just before you forget them. This method drastically reduces study time while improving long-term retention.
You can either:
✅ Create your own flashcards tailored to your needs.
✅ Download premade decks (available on the Anki website). Some are based on word frequency lists, which makes learning the most common words effortless. We highly recommend using premade decks if good ones are available for your target language. This saves a lot of time compared to making your own.
How to Choose the Right Anki Deck
Not all decks are created equal. To maximize effectiveness, look for these features:
🔹 Native speaker audio – Helps you develop correct pronunciation from the start.
🔹 Sentence-based flashcards – Instead of memorizing isolated words, learn them in context. Our brains retain information much better when it’s part of a meaningful sentence rather than a single word. If you primarily use sentence-based cards, you achieve two things at once: you’ll learn high-frequency words naturally, and you’ll absorb essential grammar structures without formal study.
🔹 Gradual difficulty increase – A good deck should start with simple sentences and build up complexity over time. Avoid decks that throw advanced grammar at you too soon. If complex grammar is unavoidable, a well-designed deck will include a note advising you to ignore it for now.
🔹 Breakdowns & explanations – Some decks include grammar explanations and sentence breakdowns, making them even more effective.
Bonus Features to Look For:
🔹 Images – If you’re a visual learner, pictures can reinforce meaning.
🔹 Context-based decks – If the deck is tied to a textbook, TV series, or structured course, it can boost retention by teaching words you are already familiar with. For example, our French and Spanish decks are based on the renowned French in Action and Destinos courses. You can watch an episode on YouTube and then review it using our Anki decks for even better results.
🚀 Want to save 50% of your study time? Check out our free PDF on Anki hacks to make the most of spaced repetition.
1.2 Grammar

Once you’ve learned the most frequent words in your target language, you’re already on the right track. But grammar plays a crucial role too—especially in languages with complex structures like Russian with its six cases or German with its noun declensions.
At the beginning, you don’t need perfect grammar to communicate. Even if you make mistakes, people will usually understand you. Instead of memorizing grammar tables, focus on:
✅ Understanding key grammar concepts
✅ Recognizing common word forms
💡 How to Learn Grammar Naturally
- The best way to absorb grammar is through an Anki deck that gradually introduces grammar with lots of example sentences.
- If your deck includes grammar explanations, that’s even better! But even if it doesn’t, a sentence-based approach will help you pick up patterns intuitively.
- If you come across sentences you don’t understand, ask ChatGPT for an explanation. This way, you get instant feedback without needing to dive into grammar textbooks.
📖 Should You Use Grammar Books?
Yes, but selectively. A traditional textbook or online course can be helpful for detailed grammar explanations, but we don’t recommend doing endless grammar drills—they’re time-consuming and tedious.
2. Develop Understanding: Immersion
Immersion is the backbone of language learning. It means surrounding yourself with your target language—watching videos, reading articles, listening to music.
To develop an intuitive understanding, you’ll need to spend countless hours immersing yourself. But this shouldn’t feel discouraging! If you choose content you enjoy, immersion won’t feel like a chore—it will be something you look forward to.
Chances are, you’re already consuming a lot of content in a language you’re proficient in. If you replace some of that with content in your target language, your progress will skyrocket.
2.1 Different Types of Immersion
Immersion can be active or passive, but either way, it requires focus.
- Passive immersion: Consuming content in your target language without interruptions—like watching a movie or listening to music without looking up words.
- Active immersion: Doing the same but pausing to look up words in a dictionary or asking ChatGPT to explain sentences.
Both methods work, and a mix of both is ideal. Choose what suits your learning style best!
💡 Important: Watching a series in your target language with subtitles in your native language is NOT immersion—you’ll focus on the translation instead of the language. Always use subtitles in your target language instead.
2.2 Comprehensible input – Finding the Right Material

The Comprehensible Input principle states that the best learning happens when content is slightly above your current level—challenging, but not overwhelming.
When transitioning from Anki decks to full immersion, you may suddenly understand much less, which can feel discouraging. But that’s completely normal! Getting comfortable with not understanding everything is a key step toward fluency.
💡 How to Find the Right Content
- Search YouTube for “(your target language) + comprehensible input” or “immersion.” Many creators make videos specifically for learners.
- Look for content with manually created subtitles in your target language. While not essential, they help a lot.
- Avoid subtitles in your native language! They prevent your brain from processing the target language.
- Try children’s shows. They use simpler vocabulary and clear pronunciation.
- Rewatch shows you already know in your target language. Since you’re familiar with the story, you can focus on the language instead.
- Enjoyment is key! If a show or video series is fun and keeps you engaged, it’s a great choice—even if it’s not the perfect level.
On platforms like Reddit, you can find recommendations from other learners on good immersion resources.
2.3 Language Reactor – A Powerful Free Tool for Immersion
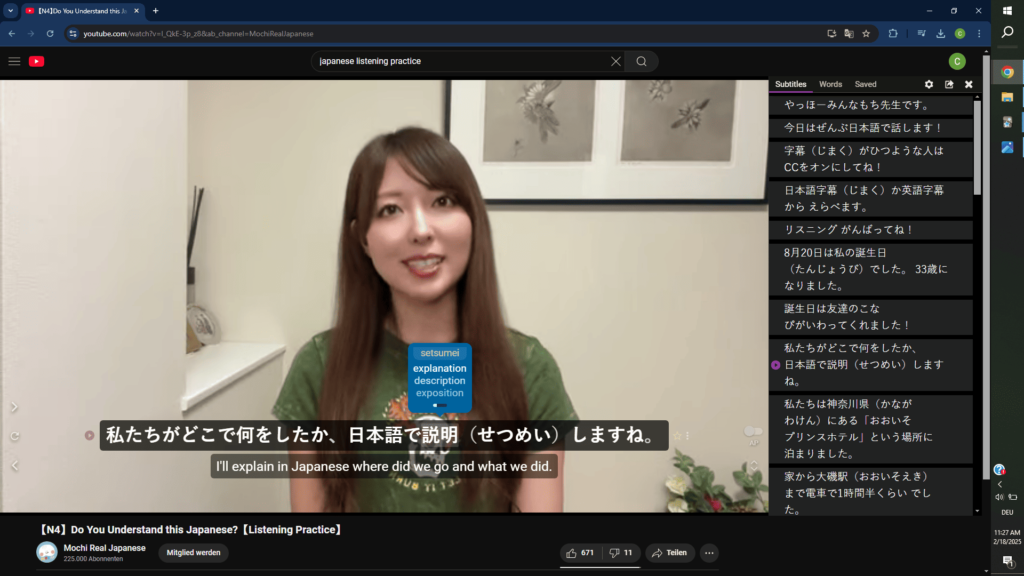
For passive immersion, all you need is content in your target language. But for active immersion, leveraging the right tools can significantly boost your learning efficiency.
One of the best free tools is Language Reactor, a browser extension that enhances immersion by providing:
✅ Pop-up dictionary – Hover over subtitles on YouTube or Netflix to see instant translations of specific words.
✅ Subtitle controls – Replay previous lines to reinforce comprehension.
✅ Pro features – Save words and sentences, and practice them in different contexts to solidify learning.
Using Language Reactor makes active immersion smoother and more effective, allowing you to quickly grasp new words and sentence structures while watching native content.
2.4 Sentence Mining – Extract & Learn
To maximize active immersion, we recommend sentence mining—a technique where you extract sentences or words from the content you consume and study them later.
How to Sentence Mine Effectively
📝 Paper & Notebook Method – Write down useful sentences while watching or reading, then review them the next day. If you enjoy handwriting, try the Goldlist method for long-term retention.
💻 Language Reactor Pro – Save words and use its built-in vocabulary trainer to reinforce learning effortlessly.
🔹 Anki Cards – Convert mined sentences into flashcards to ensure long-term retention. While manual Anki card creation can be time-consuming, using a combination of different software (like shown in this video) can make the process much faster.
2.5 Passive Listening

While focused immersion helps you understand more deeply, it can also be mentally tiring. That’s where passive listening comes in—it’s a great way to increase your exposure without the need for full concentration.
What is Passive Listening?
Passive listening means listening to your target language in the background while doing other activities. This could be while:
🚶♂️ Walking or exercising
🚗 Commuting
🥘 Cooking or doing chores
Great Resources for Passive Listening
🎙️ Podcasts for language learners – These are designed with simpler vocabulary and clearer speech.
🎵 Music in your target language – Reinforcing the same content is extremely effective, and unlike other immersion materials, you won’t get tired of listening to your favorite songs multiple times.
📺 Audio from previous immersion sessions – Listen to the audio of shows, movies, or YouTube videos you’ve already watched to reinforce familiar content.
Do You Need Passive Listening?
While passive listening is a useful tool, it’s not essential for success. You can achieve great results with just focused immersion.
In today’s world of information overload, it’s okay to choose mindfulness during daily chores instead of filling every moment with language input. The key is to enjoy the process and stay consistent.
3. Speaking

If your goal is fluency, you’ll eventually need to start speaking your target language. But when and how should you begin? Some people advocate for a “Speak from Day 1” approach, while others prefer to build a foundation first. Both methods have their pros and cons.
3.1 Speak from Day 1?
Jumping straight into conversations is a popular strategy among polyglots who aim to reach conversational fluency quickly. And this approach definitely has its benefits:
✅ Emotional engagement – Real interactions are more emotionally charged, making words and phrases easier to remember.
✅ Adaptive conversations – If people see you’re struggling, they often slow down and simplify their language, helping you understand more.
✅ Confidence boost – It’s incredibly satisfying to express yourself in a new language, which can motivate you to keep going.
However, this approach also has drawbacks:
🔹 If you’re an introvert, speaking to strangers in a language you’re not comfortable with can feel intimidating.
🔹 Conversations can be slow and frustrating at a beginner level, as you’ll need to ask for many words. This can hinder natural conversation flow.
🔹 Bad habits might form if you translate directly from your native language or make mistakes that go uncorrected. These can become ingrained over time.
3.2 When is the Right Time to Start Speaking?
If “Speak from Day 1” isn’t the right fit for you, then when should you start? It depends on your goals and circumstances:
- Living in a country where your target language is spoken? Start speaking as soon as possible to make the most of the environment.
- Learning on your own without time pressure? Consider focusing on immersion first until you’re comfortable understanding shows with subtitles. This builds a strong foundation for smoother conversations later.
- Feel ready to speak? Trust your instincts! If you feel the urge to start speaking after a few weeks of immersion, go for it—there’s no reason to wait.
💡 Key takeaway: The right moment is highly personal. Listen to your instincts, and start speaking when it feels right for you.
3.3 Ease Your Way Into Speaking
If you’re not quite ready to speak with others, don’t worry—there are several effective ways to practice output on your own. These methods help you build confidence and develop fluency without the pressure of real-time conversations.
Writing
Writing is an excellent way to practice output because it removes the pressure of thinking on the spot. You can take your time to find the right words and structure your thoughts.
How to Get Started:
📝 Diary or Journal – Write about your day or thoughts for 5 minutes a day or once a week for a longer session.
🖊️ Any Topic You Like – The key is to express yourself naturally, not to translate directly from your native language.
🔄 Get Feedback – It’s crucial to have your writing corrected. ChatGPT is great for this in many languages. If you prefer a human touch, consider using a native speaker’s help.
Chatrooms & Texting
If you want to add interaction without speaking, texting is a great next step.
Where to Practice:
💬 Language Exchange Apps – Apps like HelloTalk or Tandem allow you to find language partners and even include correction features.
🌐 Forums & Chatrooms – Engaging with native speakers in non-language learning settings is another great way to practice naturally.
💡 Tip: Teaching your language partner is rewarding but takes time away from your own practice. If you want to focus solely on your learning, chat with natives in regular communities instead.
Monologues
You don’t need another person to practice speaking—talking to yourself is surprisingly effective!
How to Practice Monologues:
🗣️ Choose a Topic – Talk about anything for a few minutes, like describing your day or discussing a hobby.
🎥 Record Yourself – This helps you review your performance and track your progress over time. You’ll be amazed at how much you improve!
🔍 Review & Learn – When you replay your recording, take note of any moments where you struggled or weren’t sure about a word. Use ChatGPT or a dictionary to look up the correct words or phrases. This way, you learn from your mistakes and expand your vocabulary.
Human Tutors
Working with a tutor is a great way to build confidence before diving into real-life conversations.
How to Get Started:
👨🏫 Find a Tutor Online – Platforms like italki or Preply offer a vast pool of qualified tutors.
🧠 Take Trial Lessons – Experiment with different tutors to find a teaching style that suits you best. A good tutor will encourage you to express yourself and correct your mistakes in a supportive way.
🔄 Practice Consistently – Regular lessons help you stay motivated and maintain a learning routine.
AI Tutors
If you’re looking for a budget-friendly and flexible option, AI tutors are a fantastic alternative.
Why Choose AI Tutors:
🤖 Talk about any topic – ChatGPT lets you practice conversations on your own terms.
🔄 Instant Corrections – Prompt the AI to correct your mistakes to improve faster.
📱 Our Favorite: Among AI tutors for language learning, we recommend Talkpal. You’ll get a few free minutes of practice every day.
3.4 Real-World Conversations
If you’ve practiced with the previous strategies, you’re likely ready to dive into real-life conversations with native speakers. Being able to talk about everyday topics in your target language is incredibly rewarding and a major milestone in your learning journey.
However, if you want to discuss a wide range of topics, things can get more complicated. You’ll need to expand your vocabulary and get comfortable using it in real conversations. Luckily, with a solid foundation and consistent practice, this becomes much easier.
Taking Conversations to the Next Level
The ability to follow and participate in fast-paced conversations, especially among multiple native speakers, is one of the highest achievements in language learning. To reach this level, you need:
✅ Fluent Expression – The ability to express all of your thoughts clearly and naturally.
✅ Advanced Comprehension – A high level of understanding, even when natives speak quickly, use slang, mumble, or interrupt each other.
💡 Challenge Ahead: In group conversations where natives no longer slow down for you, you’ll encounter fast speech, slang, and overlapping voices. But don’t get discouraged—reaching this level takes months or even years of practice.
The key is to enjoy the journey and stay consistent. Every conversation, even when challenging, helps you grow and improve.
4. Honing your skills
If you’ve followed the steps outlined so far and maintained a consistent routine, you should have a solid level of fluency in your target language. But there’s always room for improvement! Now might be the perfect time to polish specific skills and refine your abilities.
4.1 Pronunciation Practice: The Shadowing Technique

Whether or not you have a strong accent doesn’t determine your fluency. However, once you reach a certain level of fluency, you may want to work on your accent to sound more natural.
One of the most effective techniques for improving pronunciation is shadowing. This involves:
- Watching a video of someone speaking your target language.
- Repeating after them in real-time, trying to mimic their pronunciation, intonation, and rhythm as closely as possible.
- (Optional) Recording yourself – If you want to track your progress, you can record yourself and compare it to the original audio later. Alternatively, you can play back your voice in real-time using certain apps or tools. This allows you to hear your pronunciation immediately and adjust as you go.
Tips for Effective Shadowing
🔁 Consistency is Key – Shadowing can be tiring at first, but with regular practice, you’ll build stamina to do it for 10-15 minutes at a time.
🎥 Choose One Person to Shadow – It’s best to stick to one speaker whose content you enjoy and whose voice you wouldn’t mind sounding like. This avoids confusion from different speaking styles.
👫 Pick Someone Similar to You – Choosing a person of the same gender and similar age can make it easier to match their voice and intonation patterns.
Pronunciation Coach or Tutor
If you’re serious about perfecting your accent, consider investing in a pronunciation coach or working with a private teacher who can identify and correct specific sounds you struggle with.
4.2 Perfect Your Grammar
Up until now, you might not have focused heavily on grammar, except in the foundations step. And that’s perfectly fine! Focusing too much on grammar early on can slow down your progress. But at some point, you’ll want to explore the nuances of the grammar rules you’ve encountered.
Even if you’ve developed a good intuition through immersion, you might still be making grammatical mistakes without realizing it. Deepening your understanding of grammar rules will help you identify and correct these errors.
When to Focus on Grammar
📚 After Building Intuition – If you’ve already learned the most frequent words and absorbed basic grammar patterns through immersion and sentence cards, you’re ready to refine your grammar.
🔎 When You Notice Recurrent Mistakes – If you keep making similar mistakes or are unsure about certain structures, it’s time to explore the rules in depth.
How to Improve Your Grammar
- Formal Classes – At this stage, taking formal classes can be beneficial, as teachers provide structured explanations and correct your mistakes.
- Online Courses – There are many grammar-focused online courses that allow you to learn at your own pace.
- Textbook Practice – Working through a grammar textbook and doing targeted grammar drills can help solidify your understanding.
💡 Tip: Focus on reducing your mistakes rather than aiming for perfection. Continue practicing writing and have your texts corrected to reinforce correct structures.
4.3 Reading

You might wonder why reading comes so late in this framework. After all, you’ve already been reading Anki cards and subtitles from the beginning. However, reading pure text has its drawbacks:
- It lacks audio and visual cues that aid comprehension.
- It’s easier to misinterpret words or grammar without context.
That’s why we recommend using as much text with audio as possible in the earlier stages of language learning, such as subtitled videos or audiobooks with text.
Why Add Dedicated Reading Practice Now?
Despite its drawbacks, reading has several unique advantages:
📚 No Audio Needed – You can read in noisy environments or when you don’t want to use headphones.
🚀 Faster Consumption – You can process larger quantities of text in less time compared to listening.
How to Start Reading in Your Target Language
- Graded Readers – These are simplified books for language learners and are a great way to ease into reading.
- Pop-up Dictionaries – If reading on an electronic device, a pop-up dictionary is incredibly helpful for quick translations.
- Platforms like LingQ – These tools allow you to save words and review them later, integrating vocabulary learning with reading.
Transitioning to Native Literature
Eventually, you might want to read native literature. But don’t get discouraged by the leap in difficulty! Follow these tips:
📖 Start Easy – Begin with children’s books or young adult novels as they typically use simpler language.
📚 Gradually Increase Difficulty – When transitioning to adult novels, consider using a readability tool to assess the text’s difficulty.
Using the Dale-Chall Readability Score
The Dale-Chall Readability Score is a useful tool that assesses a text’s diffulty based on word familiarity and sentence length.
- How to Use It:
- Since the tool is available for English texts, use an excerpt of the English translation of the novel you want to read—about 3,000 words should do the trick.
- Use this site to calculate the Dale-Chall score.
- The score will give you a good idea of the text’s difficulty in your target language as well.
- Score Guidelines:
- Most novels for natives range from 5.5 to 8.5.
- Start with lower scores and avoid anything above 7 in the beginning.
- Work your way up gradually for a smoother learning curve.
4.4 The journey never ends

Mastering a language is a lifelong journey. Even after reaching a high level of fluency, there’s always room for improvement and new nuances to discover.
At this stage, your focus shifts to maintaining and refining your skills. Here are some ways to keep growing:
Keep Immersing Yourself
Continue surrounding yourself with your target language.
- Watch movies, read books, and engage in conversations with native speakers.
- Constant immersion prevents you from forgetting what you’ve worked so hard for.
Challenge Yourself
Step out of your comfort zone by:
- Debating complex topics, writing essays, or giving presentations in your target language.
- Exploring specialized areas you’ve always used your native language for, whether it’s finance, fashion, or technology.
- Learning a completely new skill, like gardening or playing a musical instrument, only using your target language.
Expand Your Vocabulary
No matter how advanced you are, there will always be new words and expressions to learn.
- Keep a habit of recording new words, whether through lists or Anki flashcards.
- Seek out content that challenges your vocabulary, such as advanced literature, professional articles, or podcasts.
Set New Goals
Once you’ve achieved conversational fluency, consider aiming for:
- Professional-level proficiency – Mastering industry-specific terminology.
- Perfecting your accent – Sounding more natural and native-like.
- Learning another dialect – Exploring regional variations and slang.
The possibilities are endless. Setting new challenges keeps you motivated and engaged.
Remember, language learning isn’t just about reaching a specific milestone—it’s about enjoying the process, embracing the culture, and continuously improving. Keep learning, stay curious, and most importantly, have fun with it!
Appendix: What about different alphabets?
If you’re learning a language with a different writing system, you might wonder how to approach it. Writing systems can be roughly divided into:
- Alphabets – Where symbols represent sounds.
- Logographies – Where symbols represent words or ideas.
Most languages use the Latin alphabet, but several others exist:
Alphabets
- Arabic (e.g., Arabic, Persian, Urdu)
- Cyrillic (e.g., Russian, Ukrainian, Bulgarian)
- Devanagari (e.g., Sanskrit, Hindi, Nepali)
- Kana (Japanese)
- Greek
Logographies
- Hanzi (Chinese)
- Kanji (Japanese)
- Hieroglyphs (Ancient Egyptian)
How to Approach Alphabets
If your target language uses a non-Latin alphabet, it’s best to learn it early on—consider it as step 0 in this framework. Why?
- Alphabets usually have a limited number of letters, so learning them doesn’t take long.
- You’ll probably master the alphabet in a few days, especially if you use mnemonics like the ones in our Russian Anki deck.
- Being able to read the script gives you a huge advantage, as you’ll reinforce the alphabet through all future learning steps, whether it’s reviewing Anki cards or reading subtitles during immersion.
💡 Tip: If handwriting is part of your learning journey, practice it from the start to build muscle memory.
How to Approach Logographies
On the other hand, if you’re learning a language with a logographic writing system (e.g., Chinese hanzi or Japanese kanji), the strategy is different:
- These scripts have thousands of symbols, so mastering them takes countless hours.
- We recommend focusing on spoken comprehension first, as it’s much more rewarding early on.
- Don’t get discouraged – Even native speakers spend years mastering these writing systems.
However, if you’re genuinely interested in the writing system, feel free to dive into it whenever you’re ready.
Learning Radicals: If studying Chinese or Japanese, learning radicals (the building blocks of characters) is incredibly helpful, even if you’re not focusing on reading or writing right away.
Special Case: Japanese
Japanese has three scripts: Hiragana, Katakana, and Kanji, which can be especially intimidating. Here’s how to handle them:
- Hiragana and Katakana – Learn these at an early stage, similar to other alphabets. Knowing them lets you read a lot of Japanese already, as they’re used for many native words and all loanwords.
- Kanji – Since Kanji is logographic and highly complex, it’s better to put it off until later. Focus on immersion first.


1 thought on “How to Learn Any Language like a Pro”
I enjoyed reading this article.
Definitely has alot of knowledge and tips to achieve learning more achievable in more easy ways.
Thanks.